|
Chapter 1
p.3 Work with functions that are defined
graphically, algebraically, numerically, or verbally.
p.7 Make connections among the
algebraic equation for a function, its name, and its graph.
p.15 Transform a given pre-image function
so that the result is a graph of the image function that has
been dilated by given factors and translated by given
amounts.
p.22 Given two functions, graph and
evaluate the composition of one function with the other.
p.33 Given a function, find its inverse
relations, and tell whether or not the inverse relation is a
function.
p.42 Given a function, transform it by
reflection and by applying absolute value to the function or
its argument.
p.50 Start writing a journal in which you
can record things you have learned about precalculus
mathematics and questions you have concerning concepts about
which you are not quite clear.
Chapter 2
p.61 Find the function that corresponds
to the graph in Figure 2-1b and graph it on your grapher.
p.67 Extend the definitions of sine and
cosine for any angle.
p.73 Be able to find values of the six
trigonometric functions approximately, by calculator, for
any angle and exactly for certain special angles.
p.80 Given two sides of a right triangle
or a side and an acute angle, find measurements of the other
sides and angles.
Chapter 3
p.95 Learn the meanings of amplitude,
period, phase displacement, and cycle of a sinusoidal graph.
p.96 Given any one of these sets of
information about a sinusoid, find the other two:
- the equation
- the graph
- the amplitude, period or frequency, phase displacement,
and sinusoidal axis.
p.106 Plot the graphs of the tangent,
cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions, showing their
behavior when the function value is undefined.
p.111 a. Given an angle measure in degrees,
convert it to radians, and vice versa.
b. Given angle measure in
radians, find trigonometric function values.
p.117 Learn about the circular functions
and their relationship to trigonometric functions.
p.125 Given the equation of a circular
function or trigonometric function and a particular value of
y, find specified values of x or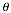 . .
p.130 Given a verbal description of a
periodic phenomenon, write an equation using the sine or
cosine function and use the equation as a mathematical model
to make predictions and interpretations about the real
world.
Chapter 4
p.157 Investigate the sum of the squares
of the cosine and sine of the same argument.
p.159 Derive algebraically three kinds of
properties expressing relationships among trigonometric
functions.
p.163 Given a trigonometric expression,
transform it into an equivalent form that is perhaps simpler
or more useful.
p.168 Find algebraically or numerically the
solutions to equations involving circular or trigonometric
sines, cosines, and tangents of one argument.
p.176 Given equations of a parametric
function, plot the graph and make conclusions about the
geometrical figure that results.
p.184 a. Plot graphs of inverse
trigonometric functions and relations.
b. Find exact values of
functions of inverse trigonometric functions.
Chapter 5
p.197 Investigate graphs formed by sums of
sines and cosines.
p.198 Derive a composite argument property
expressing cos(A–B) in terms of cosines and
sines of A and B, and use it to express a
linear combination of cosine and sine as a single cosine with
a phase displacement.
p.205 For trigonometric functions f,
derive and learn properties for
- f (–x) in terms of f (x)
- f (900 –
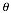 )
in terms of functions of )
in terms of functions of 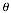 ,
or f ( ,
or f (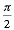 –
x) in terms of functions of x –
x) in terms of functions of x
- f (A + B) and f (A
– B) in terms of functions of A and
functions of B.
p.214 a. Given two sinusoids, form a new
graph by adding or multiplying ordinates (y-coordinates).
b.
Given a graph formed by adding or multiplying two sinusoids,
find the equations of the two sinusoids.
p.224 Transform a sum of two sinusoids into
a product of two sinusoids, and vice versa.
p.231 a. Prove that a product of sinusoids
with equal periods is also a sinusoid.
b. Derive
properties for cos 2A, sin 2A, and tan 2A
in terms of functions of A.
c.
Derive properties for cos 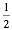 A,
sin A,
sin 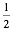 A,
and tan A,
and tan 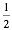 A
in terms of functions of A. A
in terms of functions of A.
Chapter 6
p.249 Given two sides and the included
angle of a triangle, find by direct measurement the third
side of the triangles.
p.250 a. Given two sides and the included
angle of a triangle, derive and use the law of cosines for
finding the third side.
b.
Given three sides of a triangle, find an angle.
p.255 Given the measures of two sides and
the included angle, find the area of the triangle.
p.259 Given the measure of an angle, the
length of the side opposite this angle, and one other piece
of information about a triangle, find the other side lengths
and angle measures.
p.263 Given two sides of a triangle and a
non-included angle, calculate the possible lengths of the
third side.
p.267 Given two vectors, add them to find
the resultant vector.
p.274 Given a real-world problem, identify
a triangle, and use the appropriate technique to calculate
unknown side lengths and angle measures.
|